Consolidated Financial Statements >
Directors’ Report
98
| 2012 annual report prysmian group
through hedging. Established commercial practice and/
or the structural characteristics of the markets concerned
mean that hedging of certain products (mainly in the Trade
& Installers business area) involves the periodic updating of
price lists (since it is not possible to use automatic sales price
adjustment mechanisms). In such cases, it is possible that,
in the current market context, the Prysmian Group would be
unable to quickly pass on the impact of fluctuations in raw
material prices to sales prices. In particular, in the case of
petroleum derivatives, it is standard practice for changes in
purchase price to systematically lag behind changes in the
petroleum price.
More generally, depending on the size and speed of copper
price fluctuations, such fluctuations may have a significant
impact on customers’ buying decisions particularly in the Trade
& Installers business area and the Power Distribution business
line and certain lines in the Industrial area more exposed to
cyclical trends in demand, and on the Group’s margins and
working capital. In particular, (i) significant, rapid increases
and decreases in the copper price may cause absolute
increases and decreases respectively in the Group’s profit
margins due to the nature of the commercial relationships
and mechanisms for determining end product prices and
(ii) increases and decreases in the copper price may cause
increases and decreases respectively in working capital (with a
consequent increase or decrease in the Group’s net debt).
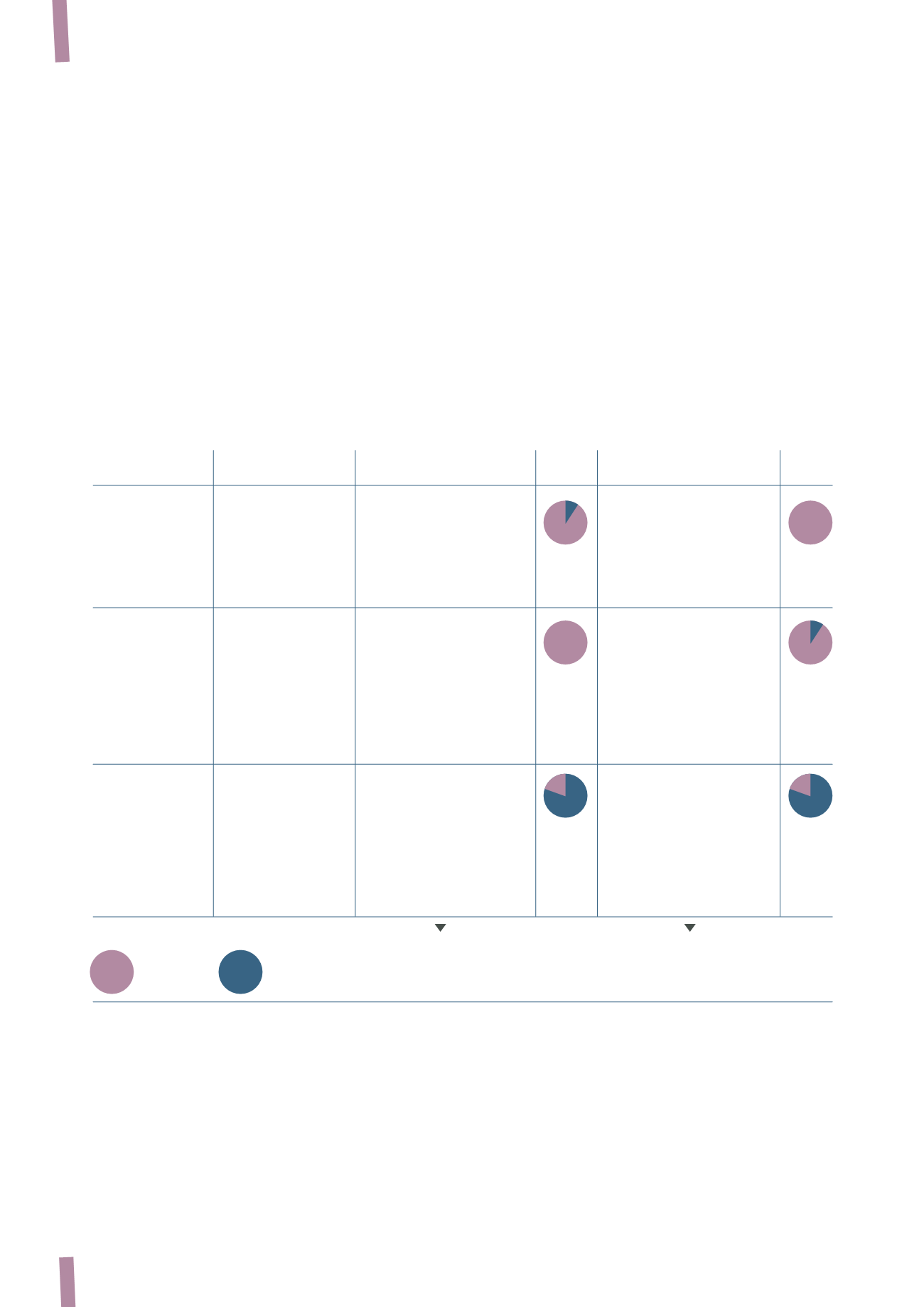
Risk hedging differs according to the type of business and
supply contract, as shown in the following diagram:
Supply Contract
Main Application
Metal influence on Cable Price Impact
Hedging of Metal Price
Impact
Fluctuations
Predetermined
Projects (Power
Technology and Design
Princing locked in at order
delivery date
trasmission)
content are the main
intake
Cables for industrial
elements of the
Profitability protection
applications (eg.OGP)
“solutions” offered.
through systematic hedging
Pricing little affected by
(long order-to-delivery
metals
cycle)
Frame contracts
Cables for Utlilities
Pricing defined as hollow
Price adjusted through
(eg. power distribution thus automatic price
formulas linked to
cables)
adjustment through
publicly avaible metal
formulas linked to
quatation (avarage last month)
publicly available metal
Profitability protection
quotation
through systematic
hedging (short
order-to-delivery cycle)
Spot orders
Cables for construction Standard products, high
Princing managed through
and civil engineering
copper content, limited
price lists (frequently
value added
updated)
Competitive pressure
may result in delayed
price adjustment.
Hedging based on forecasted
volumes rather than orders
Metal price fluctuations are normally passed through to customers
under supply contracts.
Hedging is used to systematically minimise profitability risks.
A more detailed analysis of the risk in question can be found in
the “Financial Risk Management” section of the Explanatory
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.


